Employee Experience Management (EXM)
Introduction
Employee Experience Management (EXM) refers to the strategic approach and initiatives implemented by organizations to enhance and optimize the overall experience of their employees throughout the entire employee lifecycle. It focuses on creating a positive, engaging, and supportive work environment that enables employees to thrive, remain motivated, and contribute effectively to the organization's success.
Objectives
This document aims to present a detailed and comprehensive overview of the functional and non-functional requirements for the Employee Experience Management (EXM) system. It serves as a crucial reference for all stakeholders involved in the development, implementation, and maintenance of the EXM system.
- Employee Engagement
- Continuous Learning and Development
- Feedback and Recognition
- Alignment with Organizational Values
✋ Caution
Assumptions
Here are some assumptions that could be relevant to EXM initiatives
- Users will have access to a reliable internet connection for system usage.
- The system's performance may be affected in areas with unreliable or limited internet access.
System Overview
Employee Experience Management (EXM) is an internal system focused on creating a positive and meaningful work environment for employees throughout their entire journey within an organization. It involves designing and implementing strategies to enhance the overall employee experience, from the onboarding stages to ongoing professional development and retention efforts.
🏷️Functional requirements
Functional of Employee Experience Management System:
🏷️Non-Functional requirements
Scalability
Scalability in Employee Experience Management refers to the system's capability to adapt and handle growth in the number of users, data volume, or functionalities without compromising performance. It involves accommodating increased demands efficiently and effectively, whether it's the addition of new employees, expanding functionalities, or accommodating organizational growth.
Security
Security in Employee Experience Management focuses on safeguarding sensitive employee data, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It involves implementing robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, data encryption, and compliance with relevant regulations (like GDPR or other data protection laws), to protect employee information from unauthorized access, breaches, or data leaks.
Usability
Usability pertains to the system's user-friendliness and ease of use. In Employee Experience Management, it refers to the intuitive design, navigation, and accessibility of tools and interfaces for employees. A user-friendly system ensures that employees can easily navigate, access resources, provide feedback, and engage with the platform without encountering unnecessary complexities or difficulties.
Performance
Performance in Employee Experience Management reflects the system's responsiveness, speed, and reliability in handling tasks and delivering services. It involves ensuring that the system operates efficiently, with minimal latency or downtime, even during peak usage periods. Performance also covers aspects like response times for queries, system availability, and the overall efficiency of various system functions, ensuring a smooth and seamless experience for employees interacting with the platform.
❌ Danger
Risk: Potential resistance to the adoption of the EXM system by employees.
Mitigation: Implement a robust change management and communication strategy to address concerns and educate employees about the benefits of the system.
Risk: Security vulnerabilities leading to data breaches.
Mitigation: Regularly update and patch the system to address security vulnerabilities. Implement strong access controls and encryption protocols.
User Management:
Efficiently control and organize user access to the system, ensuring secure and personalized experiences for each user with roles, permissions, and authentication mechanisms.
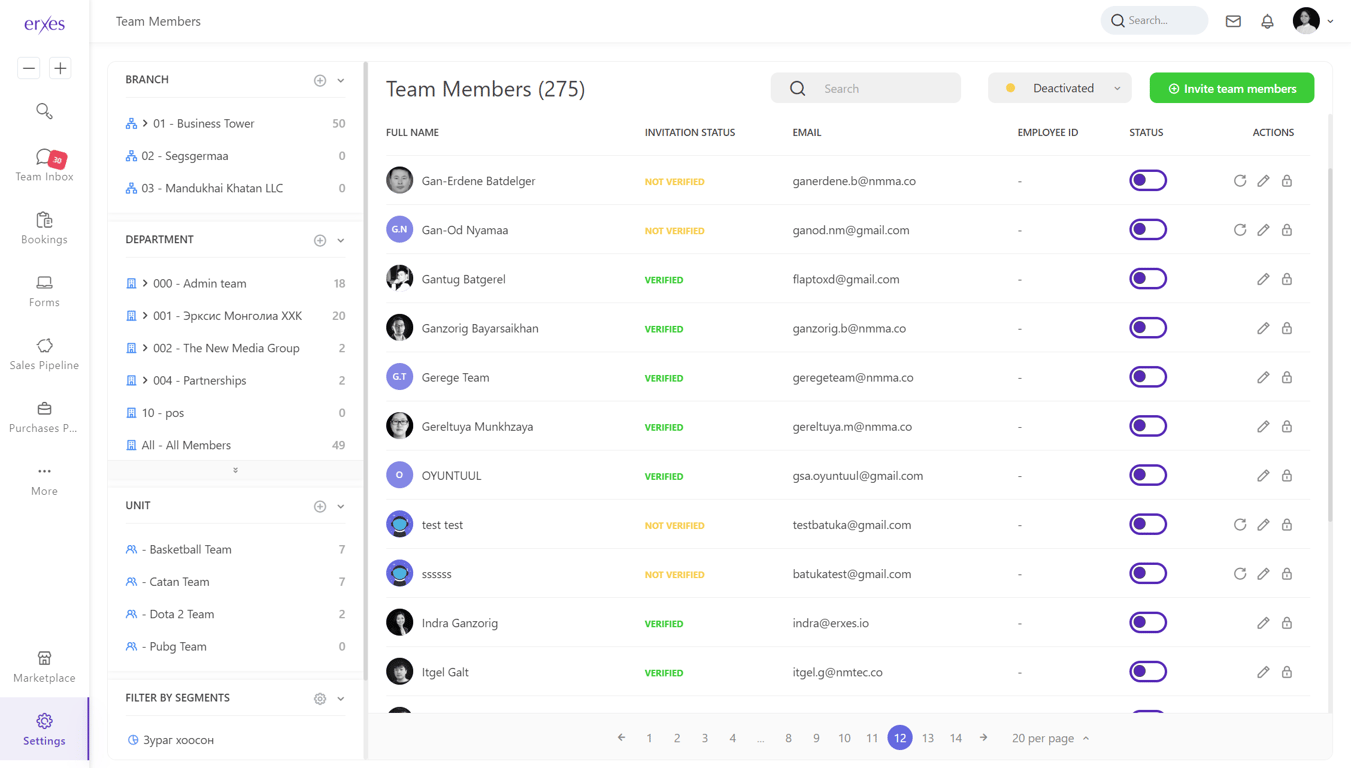
-
User Authentication:
- Secure login mechanisms.
- Password policies and encryption.
- Multi-factor authentication.
-
User Roles and Permissions:
- Define user roles (admin, manager, employee, etc.).
- Specify access levels for each role.
- Role assignment and management.
Employee database:
Maintain a comprehensive repository of employee information, including profiles, important documents, and asset records, facilitating streamlined management and easy retrieval of essential data.
ProfileEdit.png)
-
Team member profile:
- Employee information and contact details.
- Customization options for profiles.
- Add custom fields or properties.
-
Personal Documents:
- Convenient access to personal documents
- Download and print options.
-
Payslips:
- Display of salary structure.
- History of payslips.
-
Assets:
- Lists of assigned assets.
- Receive and accept assets.
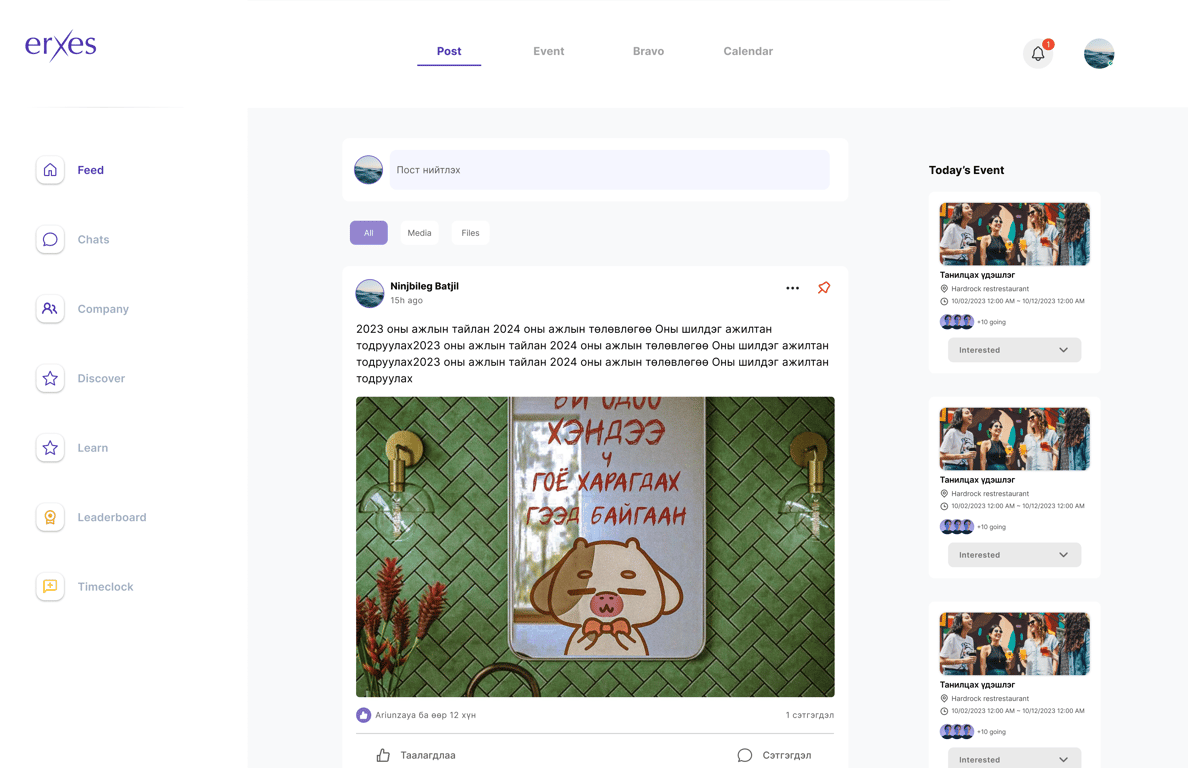
Employee engagement:
Foster a vibrant workplace culture by incorporating features such as news feeds and chat functionalities, encouraging real-time communication and collaboration among employees.
-
Internal Chat:
- Real-time messaging platform.
- Group and individual messaging.
- File sharing and attachment capabilities.
-
Feed and Calendar:
- Company-wide announcements (feeds/posts).
- Reactions and comments on announcements.
- Customizable notification preferences.
- Event reminders and alerts.
- Calendar view of the events.
-
Bravo and Thank You:
- Sending and receiving Bravo.
- Sending and receiving Thank you letters.
-
Document Sharing and Collaboration:
- Centralized document repository.
-
Requests:
- Form filling and sending.
- Compliance system.
- Survey system.
Employee Directory and Company Structure
Define and visualize the organizational hierarchy with features that enable the structuring of departments, branches, units, and teams, facilitating efficient communication and reporting within the company.
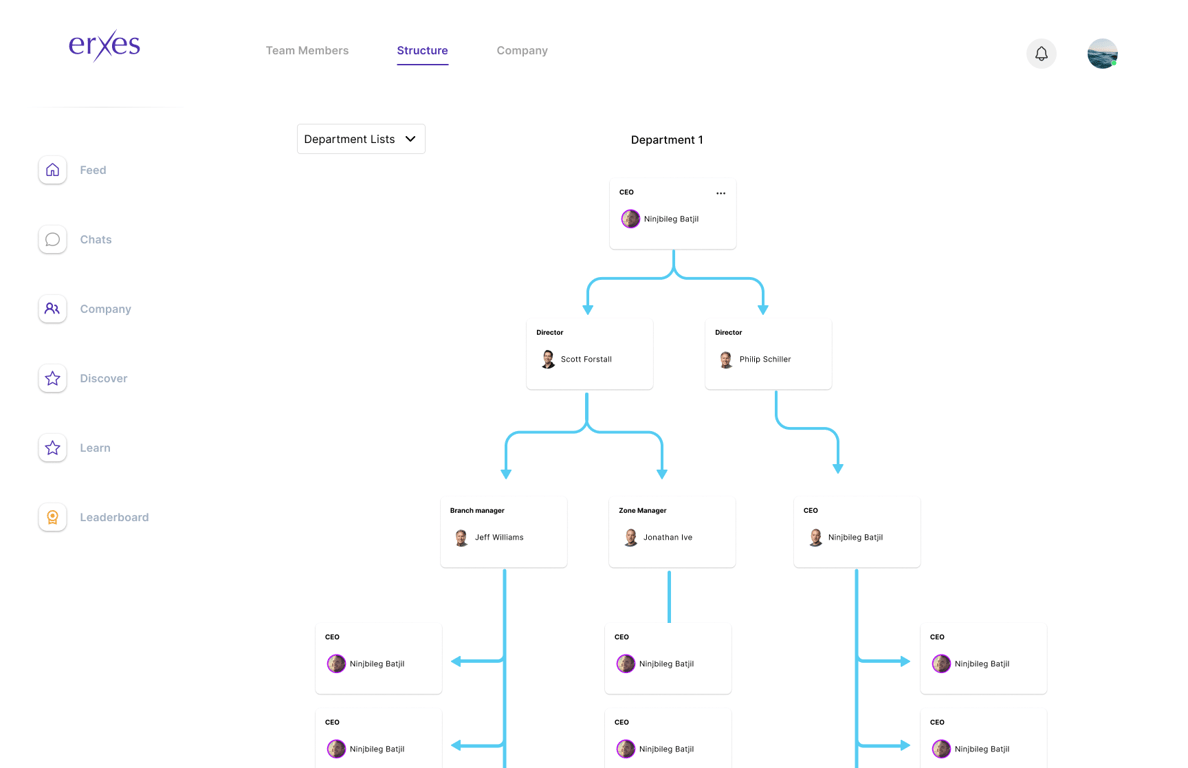
Employee directory:
- Information and contact details of all team members. Search and Filter:
- Advanced search functionality.
- Filter options based on roles, skills, etc.
- Quick access to employee profiles. Company structure:
- Organizational chart.
- Details of departments, branches, and units.
- Customization options for structure.
Leave and Attendance Management
Streamline attendance tracking with clock-in/clock-out functionalities, simplify leave requests, and manage schedules effectively, ensuring accurate and efficient monitoring of employee work hours and availability.
.png)
Timeclock:
- Leave request and approval system.
- Attendance tracking tools.
- Work schedule management tool.
Knowledge Base
-
Centralized Information Repository:
- Documented policies and procedures.
- FAQs and guides.
- Searchable knowledge base.
-
Content Management:
- Document categorization and tagging.
- User-generated content features.
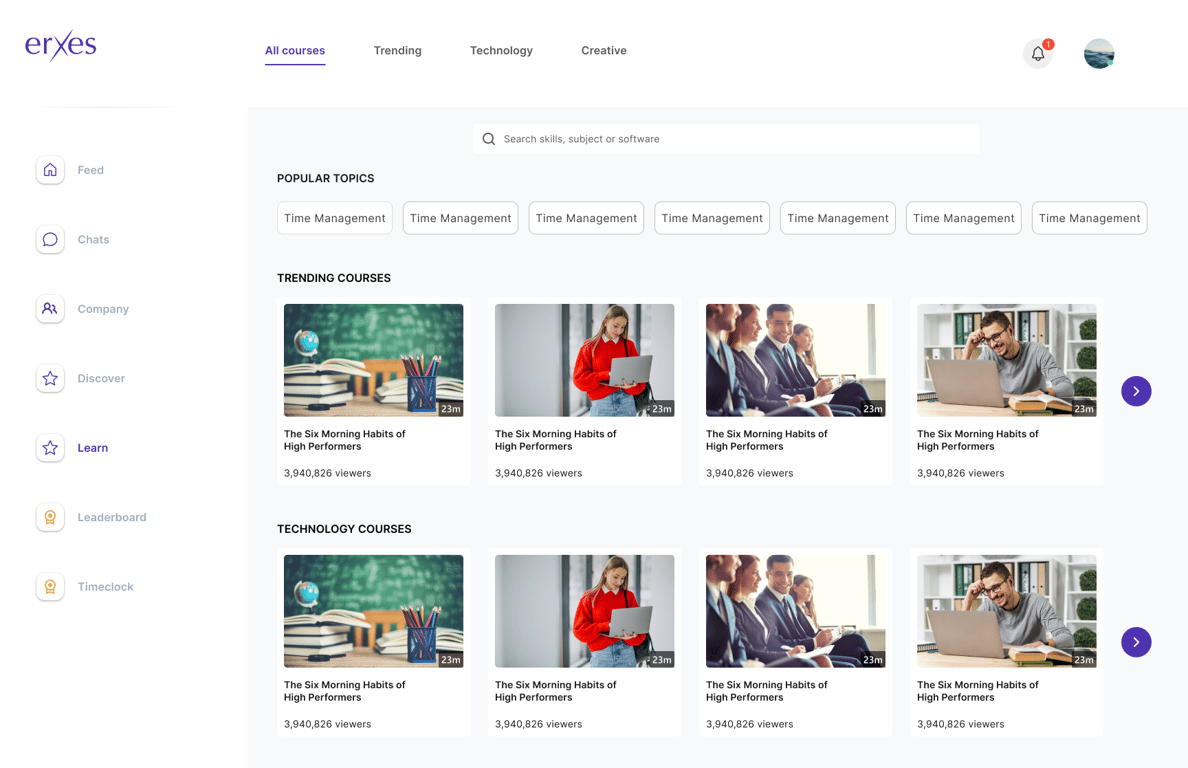
Learning and development (LMS):
Facilitate continuous employee growth and skill development through a robust Learning Management System (LMS), offering a platform for training, courses, and resources that align with organizational goals.

-
Course management:
- Program, Course, Class structure.
- Pre-requisite and dependencies.
-
Enrollment and progress tracking:
- Enrollment through LMS.
- Easy to access courses (search, filter).
- Progress tracking.
-
Development plan:
- Skill-Based Learning Paths.
- Recommended courses based on profile.
-
Assessment and Certification:
- Assessment library.
- Certification library.
- Assessment and certification integration.
-
Resource Library:
- Creation and categorization.
- Content management (text, audio, video).
-
Integration with Employee Profiles:
- Display completed courses and certifications on profile.
Reporting and Analytics
Enable data-driven decision-making with powerful analytics and reporting tools. Generate insights into employee performance, attendance patterns, and other key metrics, providing a holistic view of organizational dynamics.
- Custom Reports:
- Ad-hoc reporting capabilities.
- Customizable report templates.
- Data Visualization:
- Graphs, charts, and dashboards.
- Real-time analytics features.
Non-Functional Requirements
-
Scalability:
- Ability to accommodate company growth.
- Scalable architecture and infrastructure.
-
Security:
- Data encryption and secure transmission.
- Access control and authentication measures.
- Regular security audits.
-
Usability:
- Intuitive user interface.
- Accessibility features.
- User training and onboarding resources.
-
Performance:
- Response time expectations.
- System reliability and availability.
Assumptions
Here are some assumptions that could be relevant to EXM initiatives
- Users will have access to a reliable internet connection for system usage.
- The system's performance may be affected in areas with unreliable or limited internet access.
Risks
Risk: Potential resistance to the adoption of the EXM system by employees.
Mitigation:
- Implement a robust change management and communication strategy to address concerns and educate employees about the benefits of the system.
Risk: Security vulnerabilities leading to data breaches.
Mitigation:
- Regularly update and patch the system to address security vulnerabilities.
- Implement strong access controls and encryption protocols.